Stomata
Definition
Stomata are small pores found mainly on the surface of plant leaves and stems. They are surrounded by specialised guard cells that regulate their opening and closing. Stomata play a crucial role in gas exchange, allowing carbon dioxide to enter for photosynthesis and oxygen to exit. They also enable transpiration, the process by which water vapour leaves the plant, helping to control water balance and temperature.
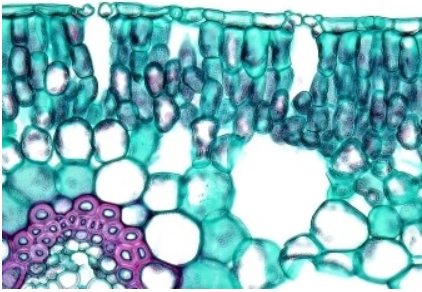
Figure 1: Stomata in the leaf. Photo: BCC Bioscience Image Library
A stoma consists of two closing cells. Below the closing cells are cavities in the mesophyll. When the relative humidity (RH) in these cavities is lower than in the greenhouse air, stomata close because the cell tension, the turgor, decreases.





