Prove and claim carbon capture in your soil
Soil Carbon Check
Soil Carbon Check is a specific soil test that provides unique data on the amount and quality of carbon captured in the soil and how this can be improved. Healthy soils store enormous amounts of carbon and play a vital role in reducing CO₂ in the atmosphere. By managing the soil wisely, farmers and growers can strengthen both climate resilience and soil fertility.
With Soil Carbon Check, you gain verifiable insight into how your soil performs today and how it can store even more carbon tomorrow. The test delivers measurable results that support sustainability reporting and reward systems for carbon capture.
Prove and claim carbon capture
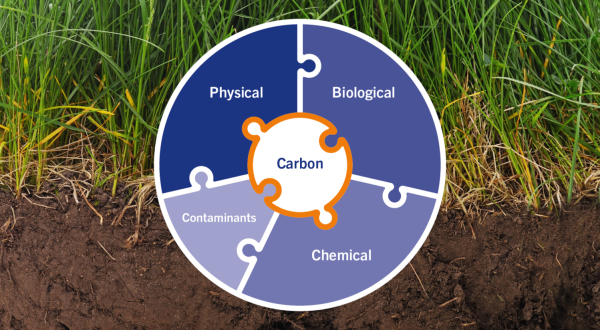
Soil organic carbon is often considered the most important element of soil health because it influences physical, chemical and biological soil components. It affects soil workability, water holding capacity, root penetrability, nutrient-binding (K, Ca, Mg), biodiversity and disease suppression.
Soil Carbon Check makes it possible to prove and claim sustainability within the agri-food chain. Various systems are being developed to reward farmers for their efforts to capture CO₂.
The test uses Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS), a fast, efficient and environmentally friendly method, to measure and monitor soil organic carbon. Regular use makes it possible to demonstrate a measurable increase in soil carbon and CO₂ removal from the atmosphere.

Carbon Calculator
Soils have great potential to store carbon and thereby contribute to climate change mitigation. How much carbon is captured in the soil largely depends on management choices – such as crop rotation, green manure, tillage and fertilisation.
The Carbon Calculator provides insight into how these factors influence carbon storage.
By entering crop plans and organic inputs (e.g. manure, compost), you can calculate the effect of your farming practices on soil carbon development.

Compatibility and recognition
Soil carbon capture helps mitigate global warming. Verra is one of the leading organisations that sets standards for climate action and sustainable development.
Soil Carbon Check is compatible with recommended methods and makes it possible to obtain recognition for verified carbon capture.
Using Soil Carbon Check data, farmers and advisers can:
- demonstrate sustainability performance within the agri-food chain
- support certification or reporting initiatives
- take part in carbon reward systems currently under development

Additional insights
Besides its climate relevance, carbon sequestration has clear agronomic benefits.
Organic matter affects:
- Physical properties: soil workability, water holding capacity, root growth
- Chemical properties: potassium-, calcium- and magnesium-binding capacity
- Biological activity: biodiversity, disease suppression, nitrogen and sulphur mineralisation
Because organic matter decomposes by around 2% per year, it is important to measure soil carbon regularly. Soil Carbon Check tracks carbon content over time and provides insight into changes in organic matter and soil fertility.

Parameters analysed in Soil Carbon Check
Each Soil Carbon Check includes key parameters that quantify and characterise soil organic carbon. Together, these parameters describe how much carbon is stored in the soil, how stable it is, and how it develops over time.









